The implications of climate change are more pronounced than ever before, and industries across the board are being called to action. Biotech, healthcare, and pharmaceutical industries are no exception. With their significant carbon footprint and resource-intensive operations, the urgent need to pivot towards sustainability within these industries cannot be overstated. A recent SLAS Symposium panel discussion, “Sustainable Excellence: Charting the Course for an Energy-Efficient Sample Storage Future,” casts a spotlight on this shift, delineating the path forward through innovative and sustainable practices.
The expert panel with representatives from four leading pharma and biotech companies discussed the various challenges and solutions their organizations have adopted to meet ever-more urgent requirements toward achieving carbon neutrality.
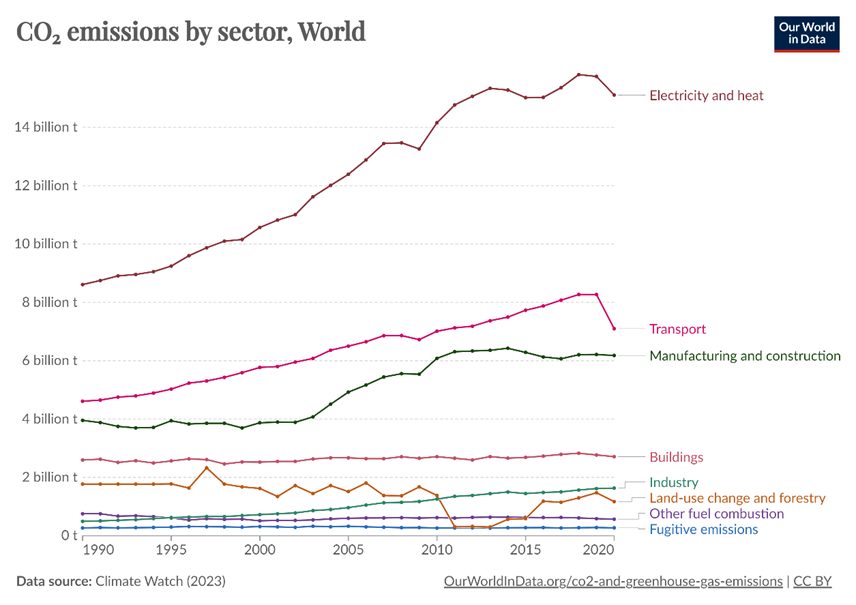
The biotech sector, particularly in its sample storage, biobanking, and broader operational practices, is at a critical juncture. As a significant contributor to global emissions and environmental impact, the industry faces the pressing need to adopt sustainable practices.
A recent My Green Lab report found that within private biotech and pharma sectors, the overall carbon impact has increased each year, rising from 3.9% in 2021 to 5% in 20221. With the biopharma industry alone responsible for 260 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e) per year, surpassing even the forestry and paper industry sector2, the push towards sustainability is not just warranted but imperative.
The Time for Sustainability Is Now
The urgency for implementing sustainable practices is underscored by the goals of the Paris Agreement and the collective push towards net-zero emissions. A growing number of pharmaceutical companies have already pledged to cut carbon emissions by at least 50% by 2030 and reach net zero by 20503.
As global regulations tighten, targeting net zero by 2050 and phasing out harmful substances like ozone-depleting chemicals, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and fluorinated gases3, the cost of inaction becomes increasingly high. The symposium underscored some major takeaways in the overall adoption of sustainability goals:
- To meet the Paris Agreement 1.5°C global warming limit3, a significant reduction (45%) in emissions by 2030 is necessary
- A growing coalition across various sectors commits to net-zero emissions by 2025, indicating a major shift towards sustainability
- Regulatory pressures are escalating, with governments enforcing strict net-zero targets by 2050
Transitioning to sustainability is no easy task for the biotech sector, since there is currently no standardized database of emissions factors that provides an easy way to calculate and track the industry’s carbon footprint4. Even so, this shift is not just environmentally crucial but also a strategic economic decision, offering long-term savings and growth opportunities.
“Global Warming Potential (GWP) is a measure of how destructive a climate pollutant is: CO2 CWP -1 Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) is the ratio of the ability of a substance to degrade ozone, to that of chlorofluorocarbon-11 (CFC-11)”
Investing in sustainable solutions now is essential to mitigate climate risks and capitalize on the economic advantages in the long run. What are the key issues that matter?
Five Trends in Biostorage Sustainability Transformation
Drawing from seminal works and the latest findings, biostorage experts at the symposium presented a comprehensive blueprint for transformation centered around five pivotal themes: energy-efficient infrastructure, sustainable refrigerants and materials, data-driven optimization, collaborative innovation, and regulatory compliance and certification. Let’s look at each of these in more detail.
1. Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
Traditionally, ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers have been the gold standard for sample storage in biotech. Manual freezers that use old-style refrigerants can be energy hogs and take up a lot of real estate. As the industry moves toward greater sustainability, freezers are increasingly evolving to adopt newer technology, use less ozone impacting refrigerants, and focus on greater efficiency. The panelists highlighted a move towards newer, energy-efficient models and alternative cooling technologies like air refrigeration, automation, and storage consolidation to mitigate environmental impacts, emphasizing:
- The necessity to slash energy consumption in laboratories and storage facilities through storage solutions and automation
- Exploring storage innovations that offer lower environmental impact
2. Sustainable Refrigerants and Materials
Transitioning to sustainable refrigerants and materials is imminent. With HFCs contributing significantly to global warming, the shift towards natural refrigerants (hydrocarbons, CO2) with lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) is crucial. The discussion highlighted the importance of utilizing eco-friendly materials in equipment construction to minimize resource depletion, advocating for:
- The adoption of natural refrigerants and biodegradable materials
- Reducing ecological impact while maintaining operational efficiency
3. Data-Driven Optimization
Harnessing data for optimizing sample storage practices is another important avenue. Automation and advanced monitoring and analytics can fine-tune freezer performance, cut energy use, and reduce waste. Robotic sample pickers, for example, eliminate the time-consuming process of searching for samples in a manual freezer. By swiftly retrieving samples with precision, robotic pickers reduce the time freezer doors are open, leading to energy conservation and operational efficiency, all while maintaining sample integrity. Automation allows for more streamlined workflows with less room for human error. The panelists discussed the role of machine learning for predictive storage needs, aiming for:
- Enhanced energy efficiency through targeted interventions
- Minimized unnecessary energy expenditure via proactive resource management
4. Collaborative Innovation
The symposium stressed the value of industry-wide collaboration in fostering sustainable practices. By pooling resources and sharing knowledge, the biotech sector can fast-track the development and adoption of sustainable technologies. This theme champions:
- The formation of consortia and partnerships to drive eco-friendly innovations
- Shared platforms for problem-solving and innovation in sustainability
5. Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape and achieving sustainability certifications are essential for advancing green practices. The experts highlighted the role of certifications like ENERGY STAR and My Green Lab® in verifying the sustainability credentials of storage facilities, emphasizing:
- The importance of adhering to sustainability standards and regulations
- The value of third-party certifications in demonstrating commitment to ecologically guided practices
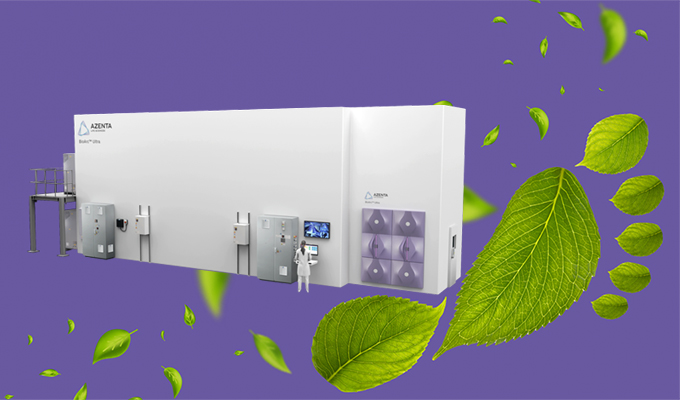
The BioArc™ Ultra: A Case Study in Sustainable Innovation
The BioArc Ultra, a state-of-the-art -80°C automated storage system, embodies the symposium’s call for sustainable biotech solutions. It stands out for its:
- Energy-efficient storage: Requires up to 73% less floor space, uses up to 77% less energy, and offers up to 79% lower Total Equivalent Warming Impact (TEWI) than equivalent manual freezers5
- High storage density: Maximized storage capacity, thereby reducing the space and energy required for sample storage
- Sustainable refrigeration: The BioArc Ultra utilizes natural air for cooling, presenting zero GWP and Ozone Depleting Potential (ODP)
- Automation for streamlined workflows: Optimized sample tracking and retrieval through automation and robotic pickers, which leads to reduced errors, energy and labor, all while maintaining sample integrity
This innovative system illustrates how the biotech sector can address sustainability challenges head-on, offering a blueprint for reducing the environmental impact of sample storage without compromising on efficiency or performance.
How much could you save?
A Clear Path Towards Sustainability in the Lab
The SLAS Symposium on sustainable practices in sample storage shines a light on the critical need for the biotech industry to embrace sustainability. Through widespread collaboration, the journey towards achieving net-zero emissions can exponentially accelerate, facilitated by the adoption and broader embrace of various technologies in the market. It’s likely that as these technologies gain increased market share, they will become more accessible and cost-effective, thus mitigating environmental pressures and benefiting all involved6. Through energy-efficient infrastructure, sustainable materials, data optimization, collaborative innovation, and strict regulatory adherence, industries may be able to significantly mitigate their environmental impact.
Learn more about shifting your laboratory to more sustainable practices with our innovative automated sample storage solutions.
References
1. “2023 Carbon Impact of Biotech and Pharma Report,” My Green Lab, 04 December 2023 : https://www.mygreenlab.org/blog-beaker/2023-carbon-impact-of-biotech-pharma-report-collective-action-accelerating-progress-to-the-un-race-to-zero
2. “2022 Carbon Impact of Biotech and Pharma Report,” My Green Lab, 11 November 2022
3. COP28, Paris Agreement, Montreal Protocol, Kigali, Amendment, US EPA AIM Law, F-gas Regulations (EU, UK, USA), UN Race to Zero
4. Decarbonising Healthcare Supply Chains, Recommendations on how to drive emissions reductions across healthcare supply chains (2022). https://a.storyblok. com/f/109506/x/1765b17e71/ smi-health-systems-supply-chains-whitepaper.pdf
5. Based on Azenta BioArc Ultra Savings Calculator Assumptions: https://www.azenta.com/bioarc-ultra-annual-savings-estimate-calculator
6. 21 Upgrading Our Systems Together: A global challenge to accelerate sectors breakthroughs for COP26 — and beyond (2021)