Automation plays a vital role in the manufacturing process of advanced therapies, yet the cold chain infrastructure has often been overlooked. While automated solutions are sometimes perceived as expensive alternatives, recent studies have demonstrated the tangible benefits of automating cold chain processes, including time efficiencies and improved process rigor.
This article explores a study conducted by the Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute (ARMI) | BioFabUSA, which quantifies the impact of cryogenic storage automation on time savings and sample quality. The study compares the results obtained from an automated system provided by Azenta Life Sciences with those obtained using a manual solution and challenges the assumption that automation in cold chain infrastructure is not worth the investment.
Methods and Experimental Setup
The study involved comparing the time requirements and sample quality of cryogenic storage using a manual LN2 Dewar and the CryoArc™ Pico from Azenta Life Sciences. The researchers monitored samples in two different shelf locations in a standard rack during rack extractions. This process was repeated using both the manual and automated setups. Additionally, the samples were examined post-thaw to identify differences in morphology that could indicate repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
“This study was undertaken as an independent evaluation by a non-profit organization to compare the effectiveness of an automated sample storage retrieval to the existing process at ARMI | BioFabUSA that relies on manual retrieval of samples – which requires staff to put on protective gear, climb up steps, and reach into a tank that contains liquid nitrogen,” said Erica Waller, product manager for the CryoArc Pico. “Using the new automated storage system, staff can skip those steps and simply enter their access information to retrieve samples from the door of the unit – which has a profile similar to a vending machine.”
“We were eager to be one of the first independent teams to evaluate a cryogenic sample workflow process that compares manual to automated retrieval,” said Sarah Boermeester, Team leader at ARMI | BioFabUSA. “The entire study was focused on determining what sort of time savings might be gained, as well as how that impacts the integrity of the samples.”

Results and Findings
The study yielded several noteworthy findings:
- Firstly, samples maintained in the automated storage system demonstrated at least an equivalent level of sample quality compared to samples stored in the manual access environment. “This finding highlights the effectiveness of automated solutions such as the CryoArc Pico in preserving sample integrity,” said Waller.
- Secondly, the time required to access samples in the automated system was significantly less than in the non-automated system. Moreover, fewer personnel and reduced personal protective equipment (PPE) were necessary when using the automated system. This not only increases operational efficiency but also enhances personnel safety.
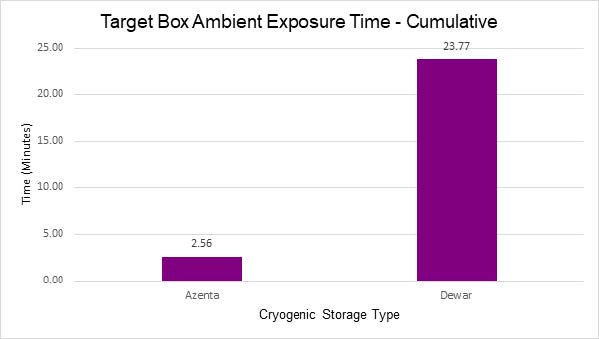
- Lastly, the risk of sample exposure to ambient conditions was significantly reduced with automation. Unlike manual access methods that often require the removal of an entire rack of samples, automated solutions enable targeted access to specific locations, minimizing the risk of exposure and potential degradation.
Implications and Benefits
The study’s findings have significant implications for cold chain infrastructure and cryogenic sample management workflows.
“Automation strengthens the quality and documentation of processes, providing controlled access and traceability of sample retrievals that supports compliance requirements. By implementing best practices and leveraging automation, facilities can optimize process control and rigor, minimizing transient warming events that can negatively impact post-thaw cell functionality and product integrity,” said Waller.
Automation also improves safety for both the staff and the samples. Staff gain an easier way to access samples, and the samples have a reduced risk of transient warming from exposure to ambient temperatures.
“Automated freezers add rigor and consistency to inventory management and material handling,” said David Lewandoski, Strategic Partnerships Manager, Automated Storage at Azenta. “Product quality is improved by minimizing transient warming events and keeping things organized.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study emphasizes the importance of considering automation in cold chain infrastructure. Contrary to common assumptions, automating cryogenic sample management workflows brings clear gains in time efficiency, data accuracy, and sample quality. The investment in automation not only streamlines processes but also improves the preservation and viability of valuable samples. As advanced therapies continue to evolve, embracing automation in the cold chain becomes increasingly vital for ensuring the success of these innovative treatments.